Local AI Under Your Control: The Possibilities of GPT4All
Imagine having your own version of ChatGPT or DeepSeek running entirely on your personal computer. The data is stored on your device — no subscriptions, no cloud servers, no third-party access. Just a fully independent, private, and customizable AI assistant.
This is the idea behind local language models. Several tools make this possible, including Ollama, vLLM, and GPT4All. In this article, we’ll focus on the latter: what GPT4All is, how it works, and why it might become your go-to solution for private AI.
How Text-Based Neural Networks Work
At the heart of every AI tool that processes text is a Large Language Model (LLM), a neural network designed to function as a kind of general linguistic intelligence. These models are capable of:
- holding natural conversations;
- analyzing data, drawing conclusions, and suggesting solutions;
- explaining complex concepts in simple terms;
- translating or adapting text to different tones and styles;
- generating, reviewing, and commenting on code.
Popular examples include the already-mentioned ChatGPT and DeepSeek, as well as Claude, Qwen, and xAI (Grok), among others.
How Local LLMs Differ from Cloud-Based Ones
The biggest advantage of cloud-based models is that all the heavy computation is conducted on the provider’s servers. Users only need a browser or an API key to access them. However, this convenience comes with trade-offs:
- Internet dependence. No network connection means no AI. The model simply won’t run offline.
- Usage limits. Cloud services often cap the number of requests, data size, or speed — especially in free tiers.
- Privacy risks. Every query goes through external servers, which can be a major concern for anyone handling sensitive data.
Local LLMs take the opposite approach. They’re smaller and optimized for full offline operation. Some of their key strengths include:
- Self-sufficiency. They run directly on your computer, independent of internet access, pricing tiers, or server queues.
- Privacy. All inputs and outputs are stored on the device. Nothing is sent to the cloud.
- Flexibility. You can switch between models for different tasks or connect your own knowledge bases.
For businesses, local LLMs mean more control, security, and autonomy. For developers, these may serve as a playground for experimentation — testing hypotheses, building prototypes, or processing documents without external limits or hidden costs.
What Makes GPT4All Useful
GPT4All is a full-fledged ecosystem for working with local language models. Think of it as an “Amuse for text”: not merely a raw engine, but a polished platform that makes interacting with AI smooth, flexible, and efficient.
The app allows you to:
- Install and run different models, from lightweight options to more advanced ones. Simply pick a language model from the catalog, download it, and start chatting.
- Work using an intuitive interface. It’s as easy as “load the model and ask a question”.
- Use your own documents to get responses based directly on their content.
How to Install GPT4All
Setting up GPT4All is quick and straightforward. Simply download the installer, run it, and complete a short setup process.
1. Go to the official website and choose the version for your operating system: Windows (.exe), macOS (.dmg), or Ubuntu (.run).
2. Install and launch the application. GPT4All automatically creates a working directory where it stores models, chat history, and settings.
3. Download a language model from the Models section or through the Find Models option on the main screen. Once downloaded, it will appear in the Installed Models library.
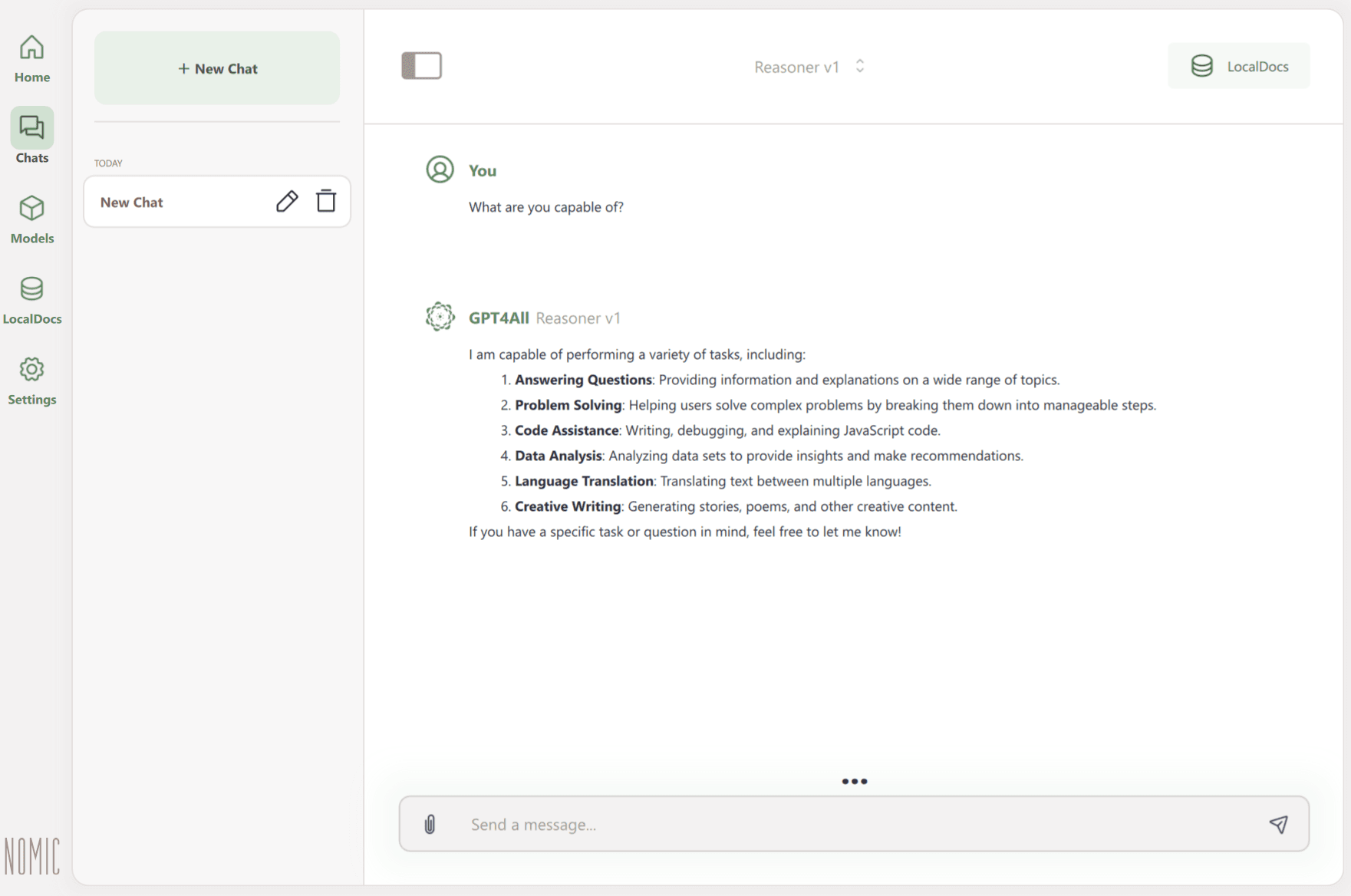
4. Start the chat. As with many cloud-based models, a prompt input field is located at the bottom, with the conversation window above it.
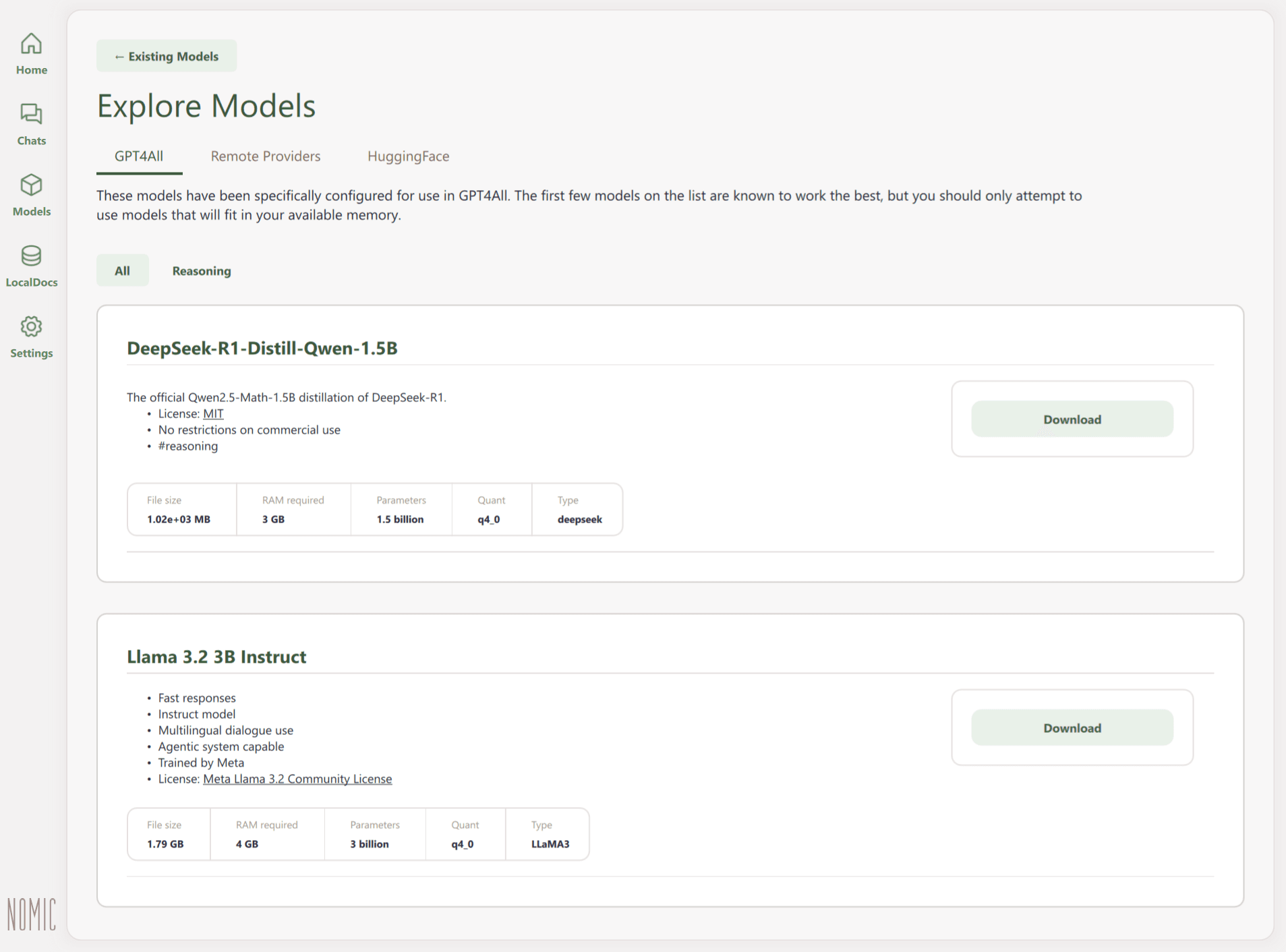
The GPT4All tab in the Explore Models section offers a catalog of models optimized for local use. Many of them run smoothly on standard CPUs; no dedicated GPU required.
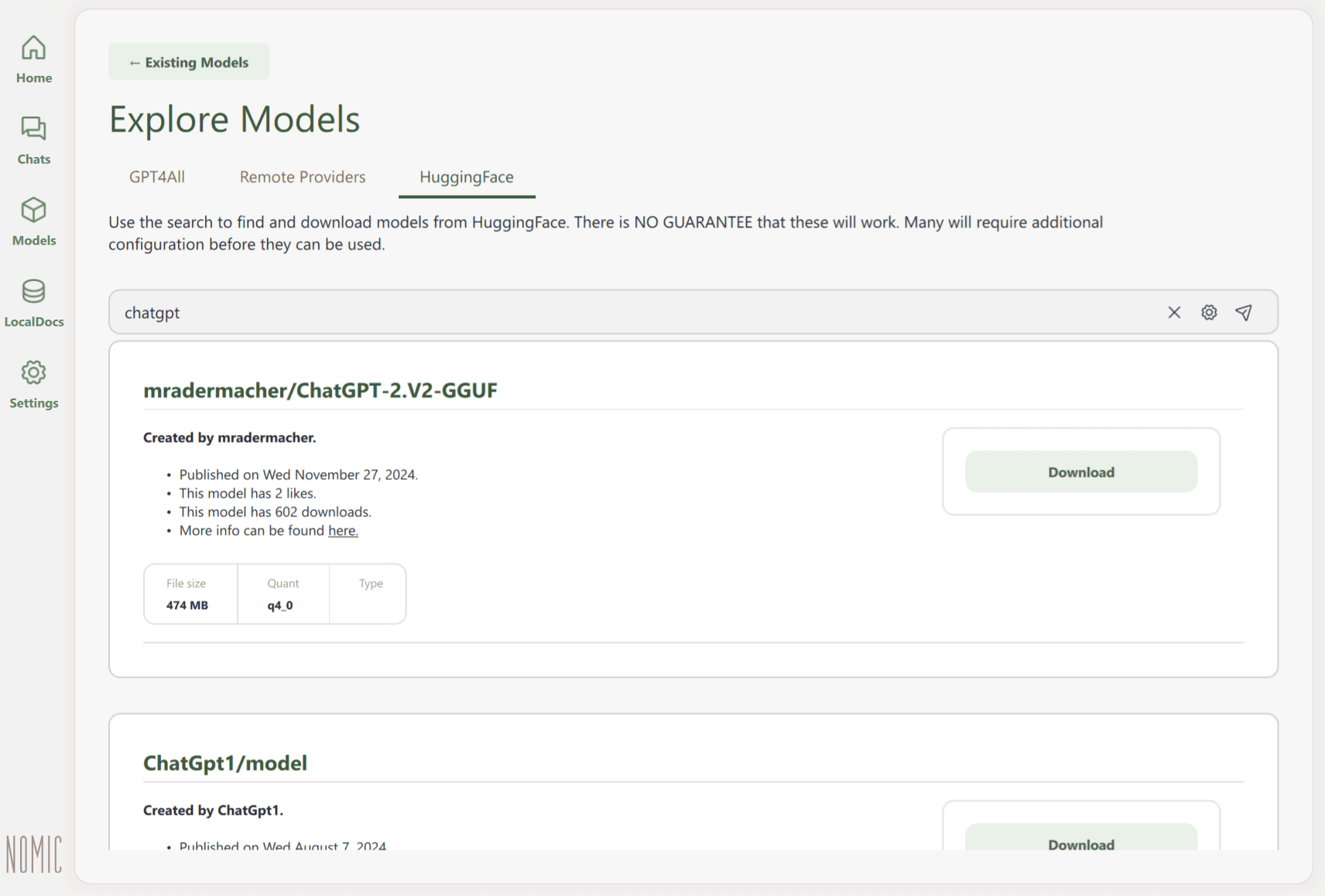
It’s also possible to browse for additional LLMs on HuggingFace through a dedicated tab. However, the developers note that external models aren’t guaranteed to work, and many of them will require extra adjustments.
GPT4All can also connect to external cloud APIs such as OpenAI, Groq, Mistral, and other OpenAI-compatible services. Though in that case, responses are generated remotely. Before enabling this feature, make sure it aligns with your privacy and data-handling policies.
Which Models Are Available for GPT4All
The GPT4All catalog includes a wide selection of language models. Some are lightweight and run comfortably on modest hardware, while others demand more resources but offer performance closer to cloud-based LLMs. Your best choice depends on the task at hand and your computer’s specs:
- Up to 4B parameters. The fastest and most lightweight models, great for short prompts or quick notes. Examples include Qwen2-1.5B-Instruct and Llama 3.2 1B / 3B Instruct.
- Around 7–8B parameters. Require more power but offer a solid balance between speed and output quality. Examples include GPT4All Falcon and Reasoner v1.
- 13B parameters and above. Resource-demanding, but capable of deeper reasoning and more coherent responses. Examples include Hermes and Snoozy.
Below are some of the most popular LLMs available in GPT4All, along with their strengths and limitations based on user feedback.
GPT4All Falcon
A very fast model based on Falcon and finetuned by Nomic AI. Simple, versatile, and perfect for exploring what the app can do.
- Strengths: fast response speed with moderate hardware requirements.
- Weaknesses: limited reasoning depth, tends to produce generic answers.
Llama 3 Instruct
A modern, flexible model from the Llama 3 family. Well-suited for open-ended chats, Q&A, and general text generation or analysis.
- Strengths: runs smoothly even without a GPU; produces logical, natural-sounding responses.
- Weaknesses: weaker reasoning compared to larger models; may lose context in longer conversations; performance varies depending on the version and quantization level.
DeepSeek R1 Distill Qwen 7B / 14B
These models are distilled versions of DeepSeek R1. The 7B model, based on Qwen2.5-Math, is optimized for analytical and logical tasks, while the 14B model is more general-purpose, offering deeper reasoning and more natural language output.
- Strengths: suitable for step-by-step reasoning, analysis, and problem-solving; the 14B version provides richer, more precise answers.
- Weaknesses: the 7B version struggles with longer reasoning chains, while the 14B model requires substantial resources (at least 16 GB of VRAM).
Reasoner v1
An experimental model focused on reasoning and code-related work. It doesn’t just output answers but performs the logical steps to reach them.
- Strengths: can analyze, infer, and test hypotheses; includes a built-in JavaScript interpreter.
- Weaknesses: may sound too formal or technical in casual conversations.
Mistral Instruct
One of the most popular mid-sized models. Trained to follow instructions precisely, answer questions clearly, and produce structured, coherent text.
- Strengths: consistent, well-organized responses with a good balance between quality and performance.
- Weaknesses: not ideal for highly technical or deeply logical tasks compared to larger models; may lose context or oversimplify reasoning; output quality depends strongly on prompt design.
Orca 2
Developed by Microsoft, this model emphasizes reasoning and step-by-step analysis. It’s intended as a compact alternative to large-scale LLMs.
- Strengths: handles logical and analytical problems effectively, producing clear and structured reasoning.
- Weaknesses: optimized for single-turn responses rather than extended dialogue; performance may vary depending on topic and prompt phrasing.
How RAG Enables Working with Your Own Documents
While large language models can process enormous amounts of data, there’s still one crucial limitation: they only “know” the information they were trained on. If a model isn’t familiar with your internal documents, policies, or manuals, it can’t reference them in its responses.
That’s where RAG, or Retrieval-Augmented Generation, comes in. This method combines two steps:
- Retrieval: finding relevant information from your own sources.
- Generation: producing an answer based on that retrieved content.
With RAG, you can connect your own files, knowledge bases, or internal documentation, allowing the model to generate answers based on your data. For example, if an employee asks, “How do I correctly submit a vacation request?”, a system powered by RAG would:
1. Locate the document describing the process.
2. Extract the relevant section.
3. Send it to the model along with the query.
4. Generate a clear, accurate response based on that material.
The result is a context-aware answer built on your organization’s internal information, not just general knowledge.
In GPT4All, RAG functionality is provided through the LocalDocs feature, which lets you create collections of documents. Simply point the app to a folder, and it will automatically index all the files it contains.
When new files are added, GPT4All breaks them into small text fragments and generates vector embeddings — mathematical representations that capture each fragment’s semantic meaning.
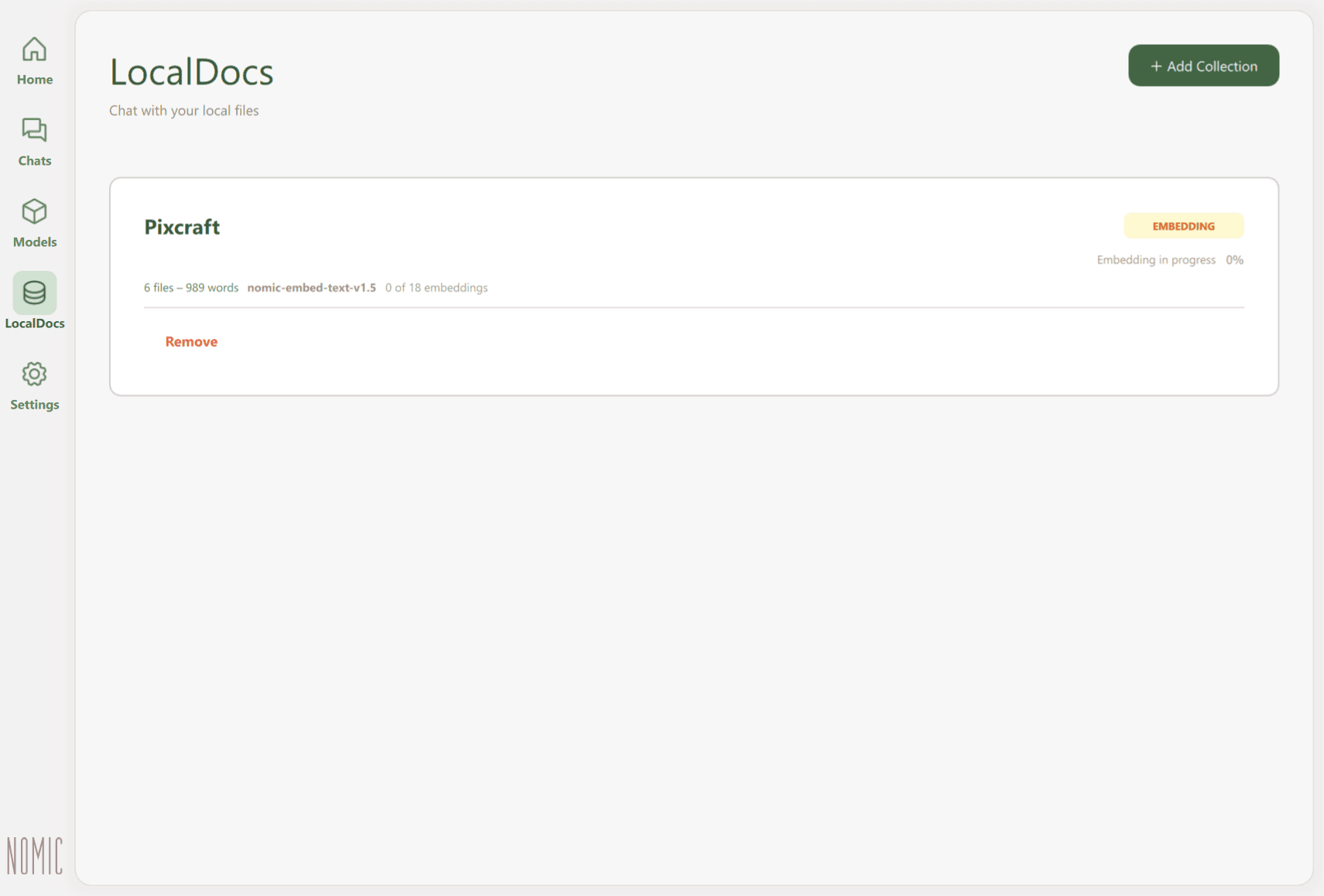
When a user submits a prompt, the system compares it to these vectors, finds the most relevant text pieces, and sends them to the model along with the original question. The model then formulates a response based on this retrieved material.
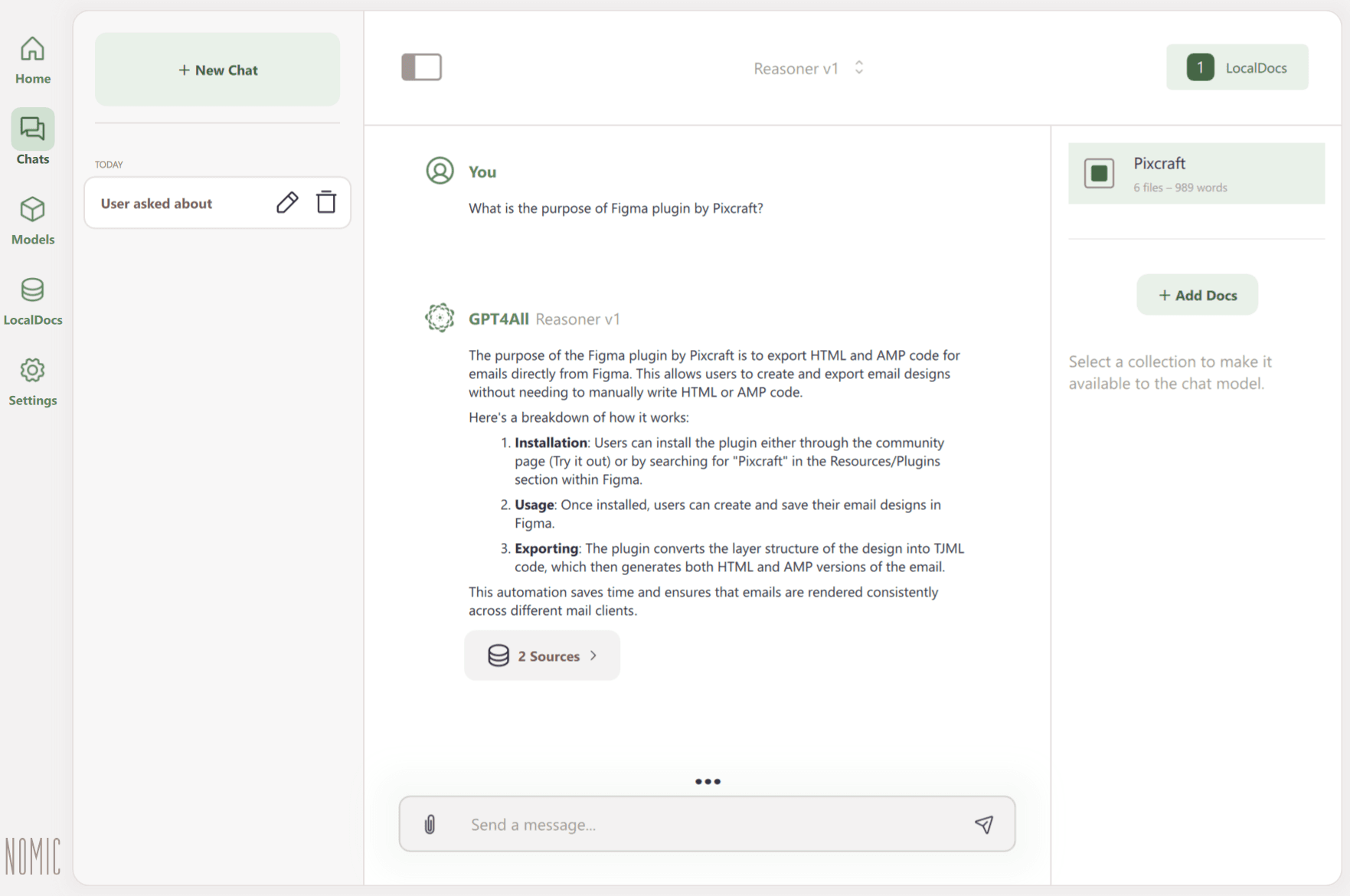
GPT4All supports text formats such as .txt and .docx, as well as PDF, and Markdown (.md). It’s important to keep text clean and well-formatted, for instance, by removing redundant Markdown symbols or formatting code. The clearer the content, the more accurate the retrieval and the final response will be.
Using GPT4All as a Local API Server
In addition to its desktop interface, GPT4All can also run as a local API server. This is especially useful if you want to integrate a local model into your company’s workflows, such as to automate text generation, document processing, or internal data analysis.
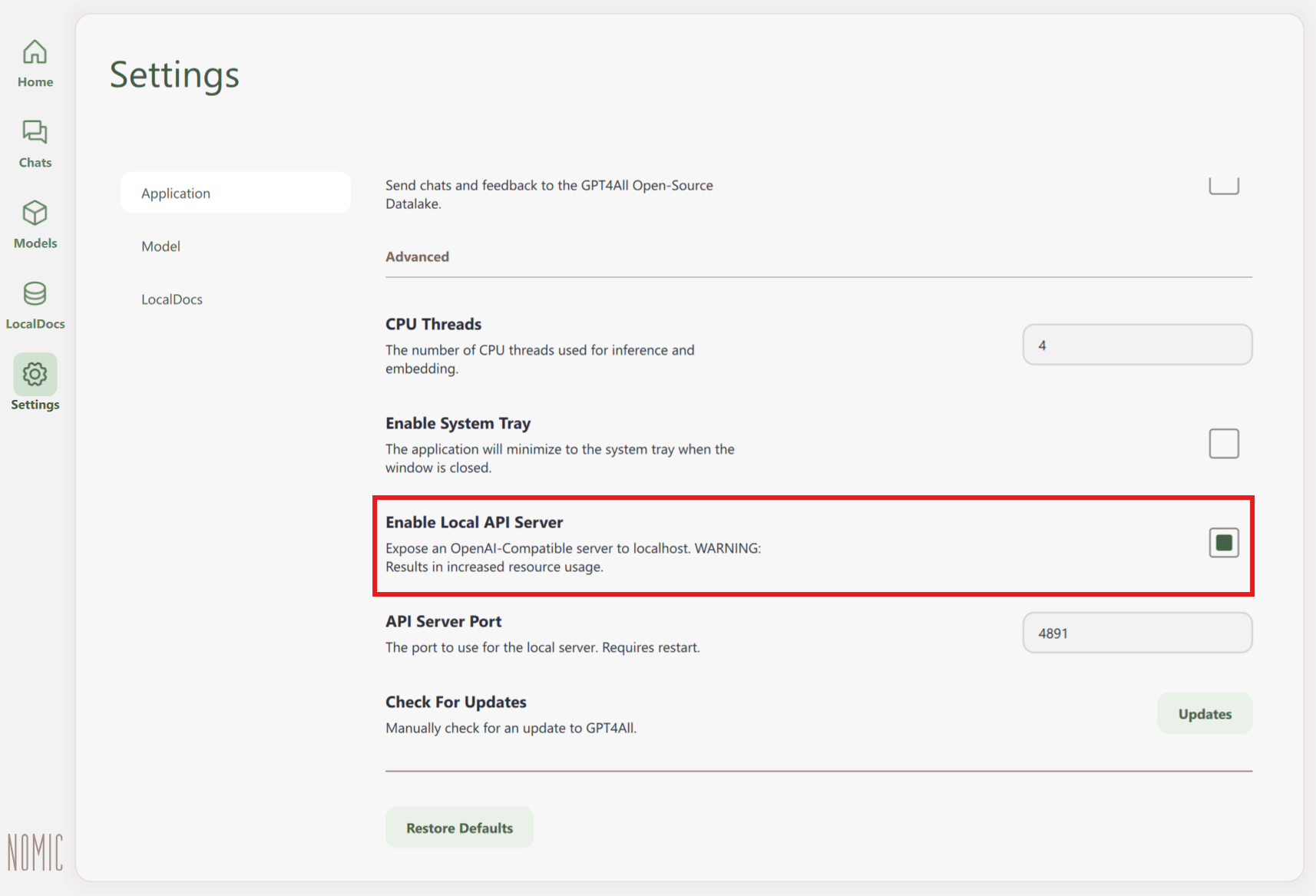
To enable the API server, follow this path:
Settings → Application → Advanced → Enable Local API Server
Once activated, the server becomes available at http://localhost:4891/v1. The number may vary depending on the chosen port.
The LocalDocs feature can also be accessed through the API. Your files never leave your computer: the API simply passes the necessary text fragments to the model so it can generate a context-aware response. Keep in mind that while the API can use existing document collections, creating and indexing new ones must be done through the app interface.
Conclusion
GPT4All puts the control over language models into your hands. It enables a truly personal form of artificial intelligence: one that runs locally, integrates into your digital workspace, and operates entirely on your terms, all without relying on cloud services, subscriptions, or external servers.
